
Volunteer or Intern in Palestine – West Bank from One Week up to three Months
Experience Palestine at Go Palestine (The Palestinian Center) in Hebron, where an array of volunteer and internship programs are designed to educate individuals about life in Palestine. Our programs cover a wide range of topics, including Media, Law, Refugees, Culture, the Palestine-Israel Conflict, Human Rights, and Healthcare.
At Go Palestine, we also provide Arabic language courses, ranging from intensive to non-intensive and super-intensive levels, catering to beginners as well as advanced learners. Our courses are taught by highly qualified and knowledgeable teachers who possess academic degrees in Arabic literature. Immerse yourself in the rich language and culture of Palestine through our language programs.
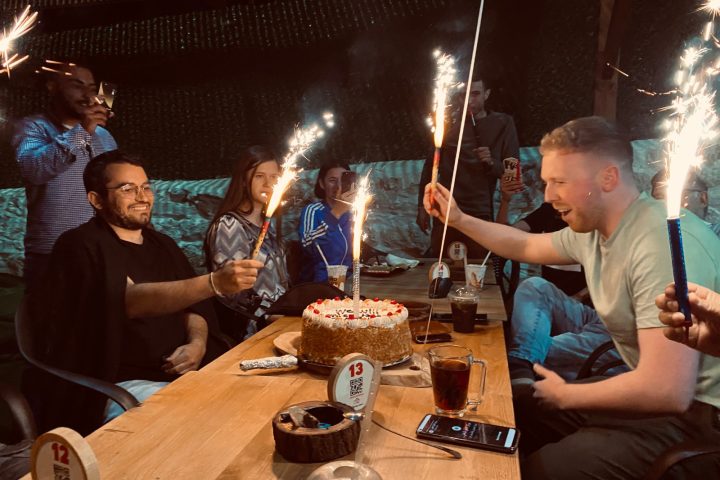
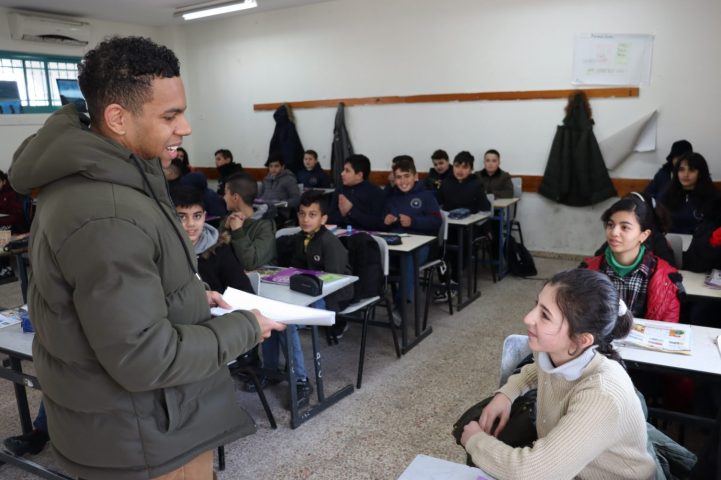
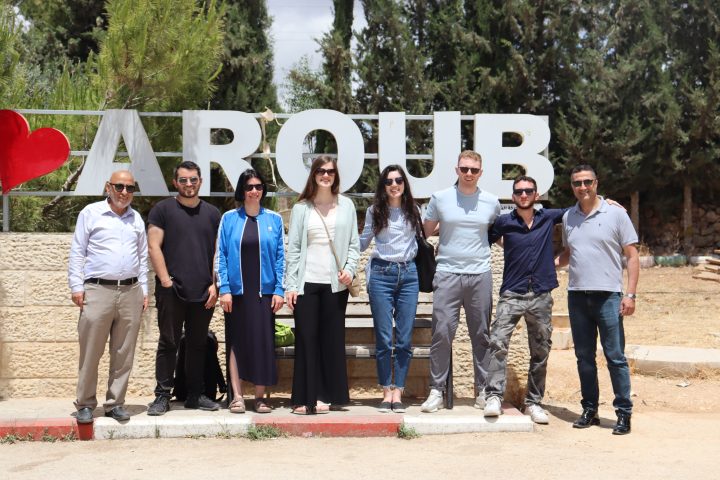
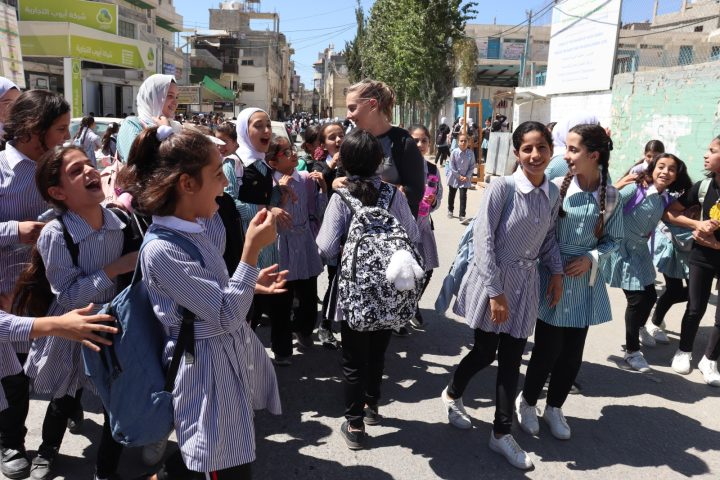

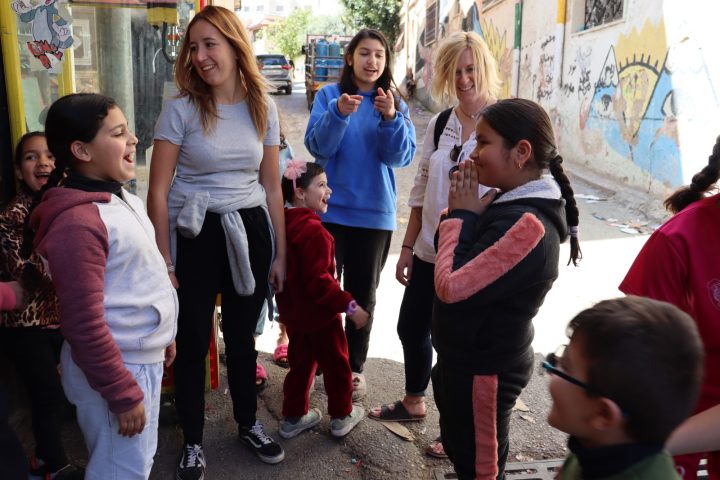



Moreover, at Go Palestine, we believe in fostering a deep understanding of the Palestinian experience. Our volunteer and internship programs offer hands-on opportunities to engage with local communities, enabling participants to witness the realities of daily life in Palestine firsthand. Whether it’s working alongside Palestinian journalists to report on important issues or assisting in legal advocacy for marginalized communities, our programs empower individuals to make a meaningful impact.
In addition to the academic and experiential aspects, Go Palestine recognizes the importance of cultural immersion. We organize cultural activities and excursions that allow participants to explore the vibrant heritage and traditions of Palestine. From visiting historical sites and landmarks to participating in traditional music and dance workshops, these experiences offer a unique perspective on Palestinian culture and foster cross-cultural exchange.
By joining Go Palestine’s programs, you not only gain valuable knowledge and skills but also become part of a supportive community passionate about promoting justice, understanding, and empowerment. Together, we strive to create a more inclusive world where the voices of Palestinians are heard and their rich cultural heritage is celebrated. Embark on this transformative journey with us and contribute to positive change in Palestine.
We hosted people coming from over 42 countries since 2011
The Palestinian Center has hosted people who have come from a myriad of countries, such as the USA, the United Kingdom, Denmark, Colombia, France, Japan, China, Chile, Switzerland, Russia, Germany, and many more. All that you need to join us is to speak English very well and have management skills.
Go Palestine welcomes all people who are 18 to 75 years old to apply to any of our volunteer/internship/language programs. Academic or professional degrees are not required to join any of our programs.
[display-map id=”10721″]
over 10 years of Experience!
Go Palestine was established to meet the cultural, social, and educational needs of the Palestinian Community. The center offers educational and community services to its Palestinian population through a diverse international staff. Through tutoring and educational programs, the center promotes unyielding support to Palestinian youth.
Go Palestine is a meeting point for all the internationals who come from every corner of the world in order to immerse themselves in Palestinian culture and become acquainted with Palestinian daily life. Our international interns and volunteers teach Palestinian youth and more mature Palestinian community members about their own home cultures, thereby gaining valuable experience and knowledge for themselves. It is a true cultural exchange.
Our Partners & Collaborators
At Go Palestine, we recognize the invaluable role played by our partners and collaborators in supporting and enriching our work. Our collaboration with a diverse array of organizations and individuals, such as local Palestinian NGOs, academic institutions, and international volunteer agencies, is essential in the creation of impactful and meaningful programs that positively affect Palestinian communities.
Our partners and collaborators bring their specialized knowledge, valuable resources, and extensive networks, allowing us to extend our reach, amplify our impact, and develop sustainable and fair initiatives. We hold great esteem for these partnerships and are dedicated to fostering enduring and robust relationships with all our partners and collaborators. Together, we have the power to bring about tangible improvements in the lives of Palestinians and contribute to the realization of a more equitable, just, and peaceful future for all.
[gslogo id=1]
Why Choose GO Palestine?
Volunteer Programs in Palestine/ the West Bank
The Palestinian Center (Go Palestine) offers the following volunteer programs. These volunteer programs address topics such as children, children with special needs, education, entertainment activities, social events, music, press Writing, community activities, workshops, and much more. Here you can do voluntary work from one week up to three months.

Volunteer with Palestinian Children (1-12 Weeks)
In this program, you will be engaging in educational and entertainment activities structured for children aged 6 to 12 years old. These activities aim to educate children with English activities.
This program has been designed to engage Palestinian children with internationals where children get to know other cultures and take part in activities that help them learn from older people in many different fields.

Volunteer with Palestinian Refugees (1-12 Weeks)
In this program, you’ll be volunteering in one of the refugee camps in the city of Hebron. The program includes organising activities for the Palestinian refugees and English classes for those who are eager to learn English.
The Volunteer with Palestinian Refugees is aimed at informing internationals with Palestinians about the refugee situation in Palestine. Through listening to the stories of Palestinian refugees, volunteers will become more knowledgeable about how the occupation has affected and still affects, their daily life.
Volunteer in the West Bank/Palestine (1-12 Weeks)
Volunteer in the West Bank program is a program in which you participate in activities that are organized to address the needs and goals of children, adults, and community members.
Volunteer in the West Bank program is one of our programs that will give you the chance to volunteer with school students, university students, and community members and, at the same time, study and practice Arabic as well as immerse yourself in Arabic culture.

Volunteer at Local Schools in Palestine (1-12 Weeks)
Volunteer at Local Schools in Palestine is a volunteer program which is offered by the Palestinian Center – Go Palestine in Hebron. This program provides a great opportunity to those who want to visit Palestine while meeting Palestinian students at the local schools in Hebron. It offers the opportunity for volunteers from all over the world to leave a positive impact on Palestinian society.

Volunteer as Articles Writer for Palestine Program (1-12 Weeks)
It’s designed for those who wish to travel to Palestine and write about it as a means of presenting the rich culture and history of Palestine. This program presents the writer with a variety of topics to choose from that tackle the life in Palestine and the other side that media doesn’t usually highlight.
Internship Programs in Palestine/the West Bank
The Palestinian Center (Go Palestine) offers the following internship programs as well. These internships focus on topics such as culture, media, politics, and law. Here you can do an internship from one week up to three months.

Internship in Palestinian Universities – West Bank (1-12 Weeks)
The Internship in Palestinian Universities – West Bank Program (1-12 Weeks) is a highly flexible and engaging program designed for individuals who are eager to explore Palestinian culture, make a meaningful contribution to the local community, and broaden their horizons. This unique program allows you to choose the duration of your internship, ranging from 1 to 12 weeks, providing you with the flexibility to customize your experience to suit your preferences and goals within the captivating West Bank region.
As part of you interning in a Palestinian universtiy, your main role will involve assisting English instructors at the university. Your primary focus will be on helping students improve their English conversation and writing skills. However, your role extends beyond the classroom as you’ll collaborate with various university departments, offering valuable support in a wide range of tasks and projects. This versatility ensures that you become an essential resource, not only within the academic sphere but also behind the scenes, contributing significantly to the overall functioning of the university.

Internship in the West Bank/Palestine Program- (Inclusive Program)
Internship in Palestine Program is an integrative program that aims to give the interns the opportunity to experience living in Palestine, learn the Arabic language, and help Palestinians by teaching English and improving their conversational skills.
Internship in Palestine Program doesn’t only include learning the Arabic language and teaching English but also includes getting to know the other aspects of Palestine, including the human rights situation in Palestine, the challenges of the Palestinian media, getting to know the Palestinian narrative of the Palestinian-Israeli conflict through field visits/trips targeting governmental and non-governmental institutions as well as meeting with activists in these three fields.

Lawyers in Palestine Internship and Study Arabic Program – Law Internship in Palestine (1-12 Weeks)
The Lawyers in Palestine Internship and Study Arabic Program is a program that gives you the opportunity to know, understand, and engage with the Palestinian legal system. As a participant in this program, you will be able to learn about the judicial system and how the courts operate in Palestine.
The lawyers in Palestine Internship and Study Arabic Program is offered at the Palestinian Center in Hebron. The program is for individuals who want to become acquainted with Palestinian law and learn how judges, prosecutors, and lawyers handle the diversity of cases that are received by the courts in Palestine.

Israeli-Palestinian Conflict & Refugees Internship Program (1-12 Weeks)
The Israeli-Palestinian Conflict & Refugees Internship (1-12 weeks) Program is an informative program that provides education and was created to inform you about one of the most complicated conflicts in recent history. The program is designed to give you a better understanding of the conflict and provide you with actual experience from the ground.
In addition, it’s a unique opportunity for participants to become acquainted with the situation of refugees living in Palestine and understand the nature of their lives inside the West Bank camps. In Hebron, we take you on field trips to the refugee camps where you will meet with families living there. It will enable participants to listen to the stories of the residents of the camps, especially the elderly who will relate how they came to be displaced into these camps.

Law and Human Rights Internship in Palestine Program (1-12 Weeks)
The Law & Human Rights Internship in Palestine Program is an informative program that provides you with information about the human rights situation in Palestine, especially Women’s and Children’s Rights and the work of human rights NGOs in the city of Hebron.
The program is designed to give you a better understanding of the situation of human rights in Palestine, including the numerous violations, and provide you with actual experience from the ground. In addition, the program gives you the opportunity to know, understand, and engage with the Palestinian legal system. As a participant in this program, you will be able to learn about the judicial system and how the courts operate in Palestine.

Media and Journalism Internship in Palestine Program (1-12 Weeks)
The Media and Journalism Internship in Palestine (1-12 weeks) is a great opportunity for individuals who are interested in media or whose work relates to media and who want to gain experience working with media in Palestine. You will have the opportunity to visit local radio stations and understand the challenges Palestinian media outlets face due to the occupation.
The Media and Journalism in Palestine will give you the chance to learn Arabic and tour a number of historic and cultural sites in the city of Hebron. Through the program, you will have the chance to produce a short film about Palestine.

Law Internship in Palestine/West Bank – Intern at a Law Firm (1-12 Weeks)
The Law internship in Palestine/West Bank program is a program that gives you the opportunity to know, understand, and engage with the Palestinian legal system. As an intern in this program, you will be able to learn about the judicial system and visit the courts in Hebron, Palestine.
The Law internship in Palestine/West Bank program is offered at a Palestinian law firm in Hebron. The program is for individuals who want to become acquainted with Palestinian law and learn how judges, prosecutors, and lawyers handle the diversity of cases that are received by the courts in Palestine.

The Education System in Palestine Internship and Study Arabic – (1-12 Weeks)
The Education System in Palestine Internship and Study Arabic (ESP) – (1-12 Weeks) aim to introduce participants to the educational system in Palestine/West Bank in public and private schools as well as UNRWA schools in the refugee camps in Hebron and Bethlehem, through field visits and meetings with school principals, teachers, and education personnel.
The ESP Internship also introduce participants to the challenges the education system faces in Palestine, both due to the occupation and the presence of two separate governments in the West Bank and Gaza Strip. The program is ideal for those who wish to learn about the structure of Palestinian schools and universities, the educational policy in Palestine, the financing issues, students educational needs, girls’ access to education in Palestine, safety of students and other aspects.

The Trade & Industry internship in Palestine Program (1-12 Weeks)
Trade & Industry internship in Palestine is designed for those wishing to learn about the most prominent industries that exist in Palestine. The program aims at introducing the participants to the factors producing the prosperity of the industrial sector, the development of sub-industries, and the formation of a cluster society. Special attention is given to the sector of shoes and leather, textiles, and clothing, which impact positively on Palestinian exports.
Trade & Industry internship in Palestine seeks to introduce participants to the commercial sector, highlighting the percentage of commercial contribution towards building the Palestinian economy, particularly in the increase of the gross domestic product. The local commercial market provides various necessary commodities. The program identifies the integrated economic relationship with the economic activities of other countries in order to achieve economic development for Palestine.
Teach English & Study Arabic in Palestine Programs

Teach English in Palestine Program (1-12 Weeks)
Teach English in Palestine is designed for those who want to teach English to Palestinians (Conversational part) and those who would love to interact with Palestinian community members in general.
In addition, this program gives a great opportunity to those who want to travel to Palestine, visit historical sites, get to know the Palestinian culture, live with a Palestinian host family, and most importantly leave a very positive impact on the Palestinian community.

Teach Conversational English & Study Arabic in Palestine (1-12 Weeks)
Teach Conversational English & Study Arabic in Palestine program is designed for those who are or who are not experienced in teaching English. For those who have little or no teaching experience, this program provides the opportunity for gaining valuable experience in teaching with the assistance of the Palestine Center’s qualified and experienced teachers.
Teach Conversational English & Study Arabic in Palestine program is designed for those who want to teach conversational English to Palestinian and those who would love to interact with Palestinian community members in general. The program offers English lessons to children aged 7-13-year-old, adults, and community members. English conversational abilities are concentrated on through the use of interactive activities.
Study Levantine or MSA Arabic in Palestine Programs

Study Shami Arabic in Palestine Program (1-12 Weeks)
The Study Shami Arabic in Palestine program presents a valuable opportunity for those who want to learn and study Shami Arabic (Levantine Arabic, also known as Ammiya) and practice it with people in Palestine.
Shami Arabic is spoken by nearly 42 million people in four Arab countries: Jordan, Palestine, Lebanon, and Syria. The Shami is the most easily understandable dialect for people of the Gulf, or Arab countries in the northernmost areas of the African continent, such as Morocco, Tunisia, Algeria, Egypt, and Libya. You will be able to communicate to a large audience of people by learning the Shami dialect.
The Learn Shami Arabic in Palestine Program presents an optimal opportunity for acquiring Arabic skills. You are provided with all the learning materials you will need, and you will be taught by our experienced and qualified teachers.

Study Modern Standard Arabic in Palestine (1-12 Weeks)
The Study Modern Standard Arabic (MSA) program in Palestine is one of the most important programs offered by the Palestinian Center to foreigners from different countries around the world who wish to learn and study Standard Arabic or the well-known modern Arabic language. The program aims to teach Modern Standard Arabic, which is the language of education, media, and journalism in the Arab world.
The program aims to provide the learner with the largest possible number of lessons and educational situations based on videos, and diverse and intensive educational activities; To be able to meet his educational needs
The Study Modern Standard Arabic (MSA) program in Palestine introduces the four language skills (listening, speaking, reading, and writing), and the elements of language (sounds, vocabulary, and structures) in an integrative way. It also takes into account the linguistic, communicative, and cultural competencies, adopting the gradual method according to the level of the learner.

Study Colloquial Arabic in Palestine (Individual Classes)
Study colloquial Arabic in Palestine Program is one of the unique programs that we offer at Go Palestine. The program was designed for those wishing to study the spoken language of the Palestinians as part of Levantine dialects. The program aims to give students the opportunity to learn the Arabic spoken language through intensive classes as well as practice the language by living with a Palestinian family in the city of Hebron.
The colloquial Arabic program is taught by qualified teachers with years of teaching experience. Our teachers use the best educational methods and techniques to teach the colloquial Arabic texts, phrases, and words that students learn in each lesson. The classes are intense in a way that makes the student get the maximum benefit during a short period of time. The program ranges from a week as the shortest period to three months as the maximum.

Intensive and Super Intensive Arabic Courses in Palestine (1-12 Weeks)
With intensive Arabic language courses in Palestine, students can learn Arabic rapidly through full immersion in both Arabic language and the Palestinian culture. Intensive courses in Modern Standard Arabic and Levantine/Ammiya Arabic are offered by the Palestinian center in Hebron, Palestine, throughout the year.
Through a variety of study options, a rich cultural immersion program, and daily practice with Arabic, students are able to quickly enhance their Arabic language skills. The duration of the course period can range from one week up to six months, depending on the student’s schedule. With excellent instructors, a wide range of cultural and language immersion activities, and a focus on total immersion in the Arabic language, the Palestinian center’s intensive Arabic courses are second to none.
ONLINE from Palestine – ONLINE Courses!
The Palestinian Center (Go Palestine) offers the following online courses:
- Online Arabic Courses including Levantine/Shami Arabic or Modern Standard Arabic (MSA)
- Teach English and Learn Arabic ONLINE!
- Online Crash Courses including different topics as Human Rights, Law, Media, Israeli-Palestinian Conflict, Healthcare, Trade & Industry in Palestine.

Study Arabic Online from Palestine (10-50 Hours)
These courses have proven to be effective in achieving the desired results. We know that there are millions of people who want to develop their Arabic skills, but they do not have the time to join an Arabic course or to travel to a foreign country.
That’s why we’ve created these online Arabic courses which means that we can aid you in your educational journey no matter what level you are or where you live. Our online program gives you all the necessary materials including radio and television programs that are aimed at improving your Arabic skills.

Learn Arabic online – Study Modern Standard Arabic ONLINE
Go Palestine offers you the chance to study Modern Standard Arabic ONLINE taught by one of our certified and professional Arabic native speaker teachers. Our Arabic online courses are comprehensive that improve your Arabic in all four skills, writing, reading, listening and speaking.
Our Online Modern Standard Arabic (MSA) courses can also be customised according to your linguistic needs or what you are looking to learn. Our highly skilled & experienced instructors who have degrees in Arabic as a foreign language guarantee quick improvement using the most recent teaching techniques and materials.

Teach English & Learn Arabic ONLINE!
If you are unable to come to Palestine for any reason, but you still want to help Palestinians by teaching English online, then Teach English & Learn Arabic ONLINE is your suitable choice. It enables you to teach English online to Palestinian students individually and at the same time learn Arabic through one of our qualified teachers.
The Teach English & Learn Arabic ONLINE is designed for those who want to teach English to Palestinians and also interact with Palestinian community members using one of the video chat apps, including Skype, WhatsApp, Google Meeting, ZOOM, and other available applications that provide such a service.

Study Palestinian Arabic ONLINE – Online With Native Teachers
Go Palestine offers you the opportunity to study Palestinian Arabic ONLINE. Our online Arabic courses will take you on a thrilling adventure while you learn Arabic using efficient teaching techniques. We’ll set you up with one of our skilled and experienced Arabic instructors to enjoy your learning journey, whether it’s for business, school, or personal enrichment, you will find what you are looking for.
Palestinian Arabic/Dialect is a dialect spoked by most Palestinians in Palestine and the Palestinian diaspora. It’s a dialect continuum comprising mutually intelligible varieties of Levantine Arabic. In two studies comparing dialects, it was discovered that Palestinian Arabic was the dialect that was most similar to Modern Standard Arabic.
Who are our volunteer & internship programs suitable for?
We at Go Palestine seek to provide internship and volunteer programs in Palestine, West Bank that suit everyone & achieve their expectations/goals of visiting and staying in Palestine. Our volunteer and internship programs in Palestine are suitable for everyone between the ages of 18- 75-year-old, which makes it available to:
- Students of universities, colleges and institutions of higher education.
- Graduates and postgraduates students.
- Academic researchers & field Researchers.
- Students who are working on writing their Master’s or PhD dissertations on topics related to Palestine or Middle East.
- Students are searching for internship or volunteer places in Palestine required by their university or college. University Credit is available.
- Gap year students who are looking to do a volunteer or an internship in Palestine.
- Students of Arabic literature, Arab studies, and cultural studies related to Arab and Middle Eastern culture.
- Students of Middle Eastern studies, Islamic studies, or studies related to the Middle East region or relevant studies.
- Anyone who is an eager to learn about different aspects of life in Palestine.
Who is eligible to apply ?
- The Palestinian Center has hosted people who have come from a myriad of countries, such as the USA, the United Kingdom, Denmark, Colombia, France, Japan, China, Chile, Switzerland, Russia, Germany, and many more.
- Anyone between the ages of 18 to 75 can register and participate in our volunteer work or internships. All nationalities and university majors are welcome (no university degrees are required).
- Those who are younger than 18 years old can also apply but with one condition. One of your parents has to fill out and sign a parental consent form.
Traveling Solo to Palestine
Traveling to Palestine, whether with someone or alone, is an interesting and once-in-a-lifetime adventure. Safety is always a concern no matter where you travel, but with common sense and planning, your travel can be enjoyable, fun, and worry-free, as well as save your money.
People in Palestine are very friendly, enthusiastic, and eager to help and to talk to people from different cultures and countries. The opportunities to interact with internationals will make the day for a Palestinian, and, in turn, this will make your trip more enjoyable and interesting. If you are traveling alone, your solitariness will make you more approachable than if you are traveling as a group member.
Do not let your fears and apprehensions paralyze you and rob you of the adventure of a lifetime. Come to Palestine as a solitary traveler and experience its fascinations and beauties. It has been said that “the world is a book, and those who do not travel read only a page”. Allow yourself to read the whole book – a book you will never forget!
How Do I Get A Visa To Enter Palestine?
What can be added to your volunteer program? “EXTRAS“
- Additional hours of Arabic language over the specified hours per week for $20 per additional hour.
- Private tours to other cities in Palestine including Ramallah, Nablus, Jenin and Jericho. Click HERE to learn more about the tours organised by Go Palestine.
- Pick-up and drop-off service from Ben Gurion Airport directly to Hebron within an hour and a half. The cost of the service is 130 USD (one way).
- A place for your friend or partner to live in Hebron, in our apartment in Hebron, or with a Palestinian family. Click HERE to check our hostel & private apartment in Hebron.
Documents you’ll receive from us!

